Microsoft NLB VMware Alternative: Multicast and Unicast Issues Solved
SafeKit Proposes a SANless Farm Cluster with Load Balancing on Virtual IP
Microsoft NLB multicast mode
As explained in the knowledge base of VMware on network load balancing (NLB) multicast mode configuration, you need to manually configure static ARP resolution at the switch or router for each port that connects to the cluster. Deployment of the Microsoft NLB multicast mode in an unknown network environment can prove to be a complex and strenuous task.
Microsoft NLB unicast mode
With Microsoft NLB unicast mode, you must configure the ESXi/ESX host to not send RARP packets when any of its virtual machines is powered on. That's why, Microsoft NLB is not working properly in Unicast Mode with VMware.
Alternative with SafeKit
The SafeKit virtual IP address configuration does not require any special network configuration and the network load balancing can run in any environment. An important feature when the solution must be deployed in an unknown infrastructure: unknown switches or routers, physical servers or virtual servers.
How the SafeKit farm cluster works with Windows?
Virtual IP address in a farm cluster
On the previous figure, the Windows application is running on the 3 servers (3 is an example, it can be 2 or more). Users are connected to a virtual IP address.
The virtual IP address is configured locally on each server in the farm cluster.
The input traffic to the virtual IP address is received by all the servers and split among them by a network filter inside each server's kernel.
SafeKit detects hardware and software failures, reconfigures network filters in the event of a failure, and offers configurable application checkers and recovery scripts.
Load balancing in a network filter
The network load balancing algorithm inside the network filter is based on the identity of the client packets (client IP address, client TCP port). Depending on the identity of the client packet input, only one filter in a server accepts the packet; the other filters in other servers reject it.
Once a packet is accepted by the filter on a server, only the CPU and memory of this server are used by the Windows application that responds to the request of the client. The output messages are sent directly from the application server to the client.
If a server fails, the farm heartbeat protocol reconfigures the filters in the network load balancing cluster to re-balance the traffic on the remaining available servers.
Stateful or stateless applications
With a stateful Windows application, there is session affinity. The same client must be connected to the same server on multiple TCP sessions to retrieve its context on the server. In this case, the SafeKit load balancing rule is configured on the client IP address. Thus, the same client is always connected to the same server on multiple TCP sessions. And different clients are distributed across different servers in the farm.
With a stateless Windows application, there is no session affinity. The same client can be connected to different servers in the farm on multiple TCP sessions. There is no context stored locally on a server from one session to another. In this case, the SafeKit load balancing rule is configured on the TCP client session identity. This configuration is the one which is the best for distributing sessions between servers, but it requires a TCP service without session affinity.
How to configure a SafeKit farm cluster?
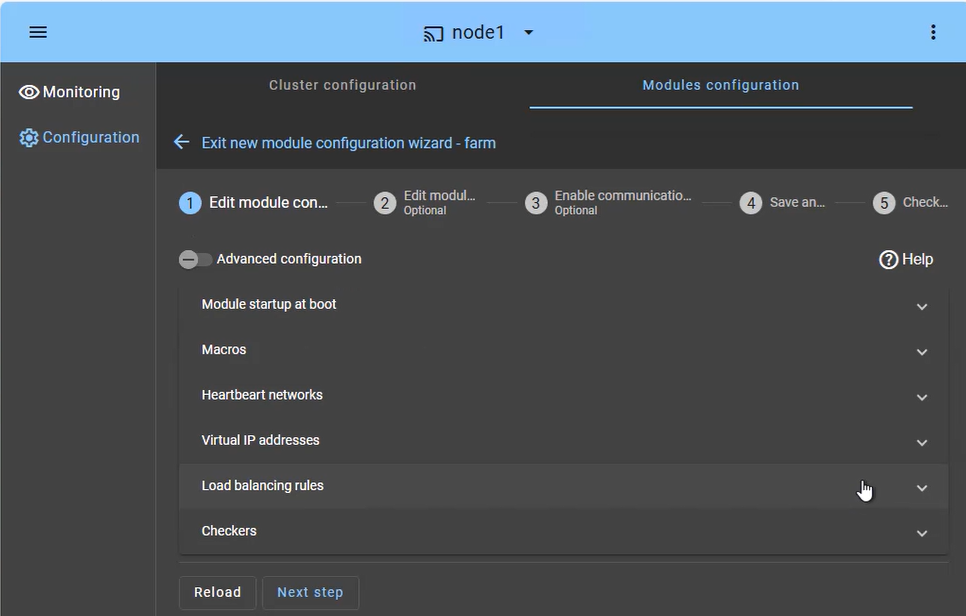
The SafeKit farm cluster is designed for high availability and scalability of services. The configuration focuses on distributing incoming traffic across both nodes simultaneously:
- Load Balanced Services (Macros tab): Define the specific application services (e.g., Apache, IIS, Nginx) to be kept active on all nodes.
- Heartbeat network(s): Communication path(s) used to detect if a node has left the farm, triggering an immediate redistribution of the load.
- Virtual IP (Farm VIP): Unlike a mirror cluster, the Farm VIP is shared between nodes using kernel filtering algorithm to distribute network traffic.
- Load Balancing Rules: Define the traffic distribution policy based on the source IP address or port.
- Checkers: Monitor the application's health and trigger automatic restart if a process failure is detected.
How to monitor a SafeKit farm cluster?
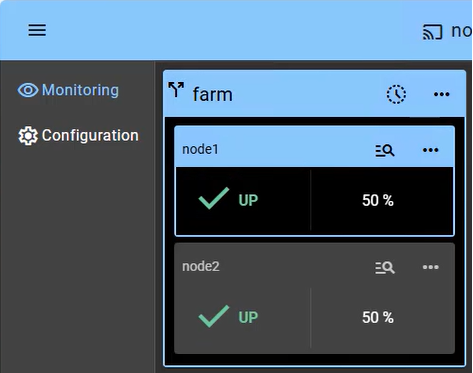
Monitoring a farm cluster provides visibility into the Active-Active nature of the infrastructure, where all nodes contribute to the application's performance (showing 2 nodes in this example):
- UP State (50% on 2 nodes): In a healthy farm, both nodes are in the "UP" (50%) state, meaning they are both actively receiving and processing client requests via the shared Virtual IP.
- Automatic Re-balancing: If one node fails, the console visually shows the remaining node taking 100% of the traffic. There is no "failover" delay, as the surviving node is already active (aside from a detection time of a few seconds).
- Node Insertion: When a repaired node is restarted, it transitions from "STOP" to "UP" and automatically starts receiving its portion of the load without administrator intervention.
- No Data Sync: Note that in a farm cluster, there is no "Orange" resynchronization state, as nodes are expected to be stateless or share a backend database (which can be protected separately in a mirror cluster).
Beyond simple status icons, the interface provides one-click node management, allowing you to manually stop or start a node for planned maintenance while the shared Virtual IP automatically redistributes traffic without interrupting user activity.
🔍 SafeKit High Availability Navigation Hub
| Resource Type | Description | Direct Link |
|---|---|---|
| Key Features | Why Choose SafeKit for Simple and Cost-Effective High Availability? | See Why Choose SafeKit for High Availability |
| Deployment Model | All-in-One SANless HA: Shared-Nothing Software Clustering | See SafeKit All-in-One SANless HA |
| Partners | SafeKit: The Benchmark in High Availability for Partners | See Why SafeKit Is the HA Benchmark for Partners |
| HA Strategies | SafeKit: Infrastructure (VM) vs. Application-Level High Availability | See SafeKit HA & Redundancy: VM vs. Application Level |
| Technical Specifications | Technical Limitations for SafeKit Clustering | See SafeKit High Availability Limitations |
| Proof of Concept | SafeKit: High Availability Configuration & Failover Demos | See SafeKit Failover Tutorials |
| Architecture | How the SafeKit Mirror Cluster works (Real-Time Replication & Failover) | See SafeKit Mirror Cluster: Real-Time Replication & Failover |
| Architecture | How the SafeKit Farm Cluster works (Network Load Balancing & Failover) | See SafeKit Farm Cluster: Network Load Balancing & Failover |
| Competitive Advantages | Comparison: SafeKit vs. Traditional High Availability (HA) Clusters | See SafeKit vs. Traditional HA Cluster Comparison |
| Technical Resources | SafeKit High Availability: Documentation, Downloads & Trial | See SafeKit HA Free Trial & Technical Documentation |
| Pre-configured Solutions | SafeKit Application Module Library: Ready-to-Use HA Solutions | See SafeKit High Availability Application Modules |
